Why is financial reporting important?
Financial reports reflect the state of your business.
Where is the business heading? How much money do you have to work with? What can you afford?
These questions and more can all be answered by examining an organization’s financial statements.
Financial reporting and analysis teams play a crucial role in organizations. While the CEO, CFO, and board of directors make decisions, FP&A provides them with the financial information they need to determine what steps to take. The financial reporting and planning team analyses report from the accounting team and use market trends to predict how the organization will perform within a month, quarter or year. Financial planning and analysis are responsible for analyzing the numbers and producing quite a few reports that are meant to assist decision-makers in getting a better understanding of the financial and operational stance of the organization.
Should we buy a new forklift? Will we surpass our budget? By how much?
Financial reporting and analysis is the process of determining how your company will afford to achieve its vision, strategic goals, and objectives.
What is financial reporting?
Financial reports are the records of any of the financial activities of a business. Company financial metrics include profits, capital, expenses, revenue, and cash flow. It’s only by looking at their financial statements that an organization can tell where their business stands and answer some important questions – how much cash do we have? Can we pay our bills? Are we making money?
For both private and public companies, financial reporting must be in accordance with GAAP regulations. This can vary by location, but each country has its set of regulations. For example, the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is used by over 110 countries in the world.
What financial reports does FP&A deal with?
There are three main kinds of financial reports that organizations produce and FP&A deals with:
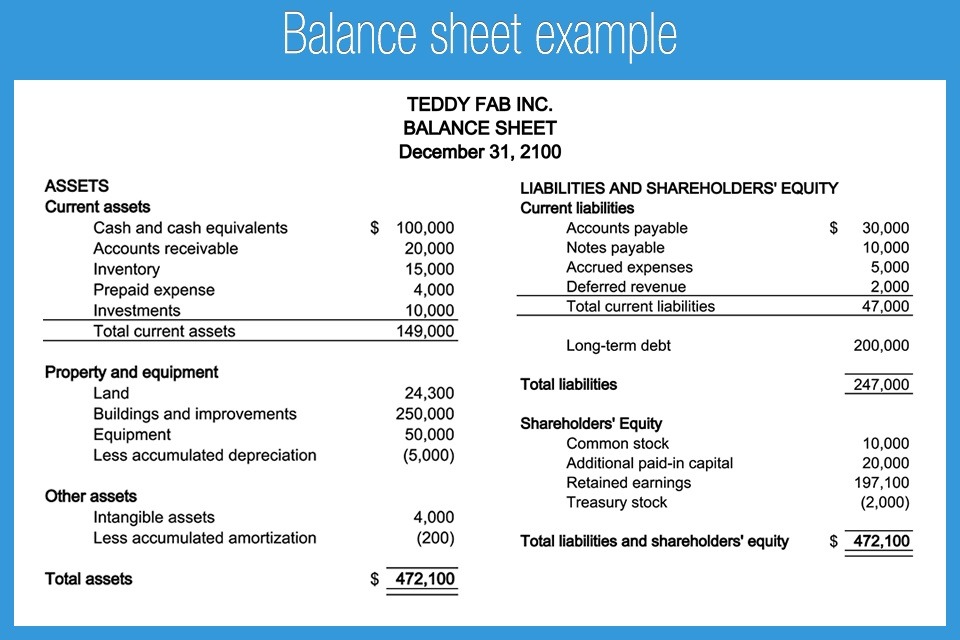
1. Balance sheet
A balance sheet is a financial report that summarizes an organization’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders equity for a particular period of time. What this means is that the balance sheet provides a picture regarding what the organization owes and owns for a particular time frame. This is important as the balance sheet report reflects the organizations status and can give you an indication of its financial stance.
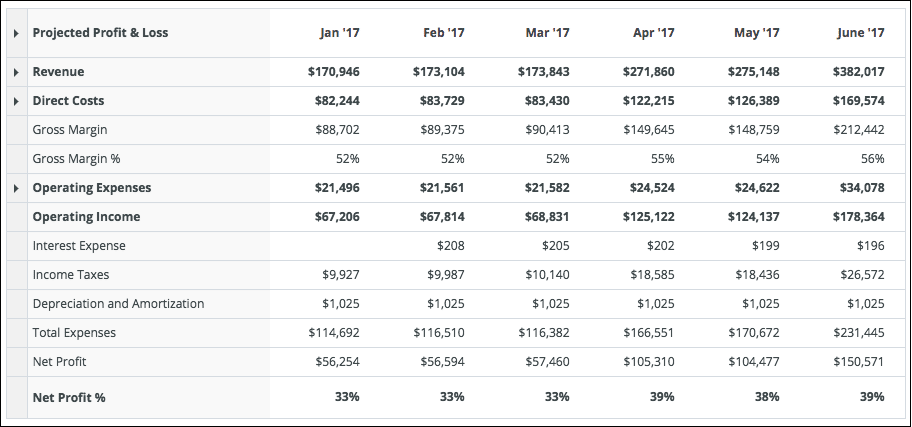
2. Profit and loss report (P+L)
A profit and loss report is a financial statement that summaries the expenses, costs, and revenues of an organization during a particular period of time, often a quarter or year.
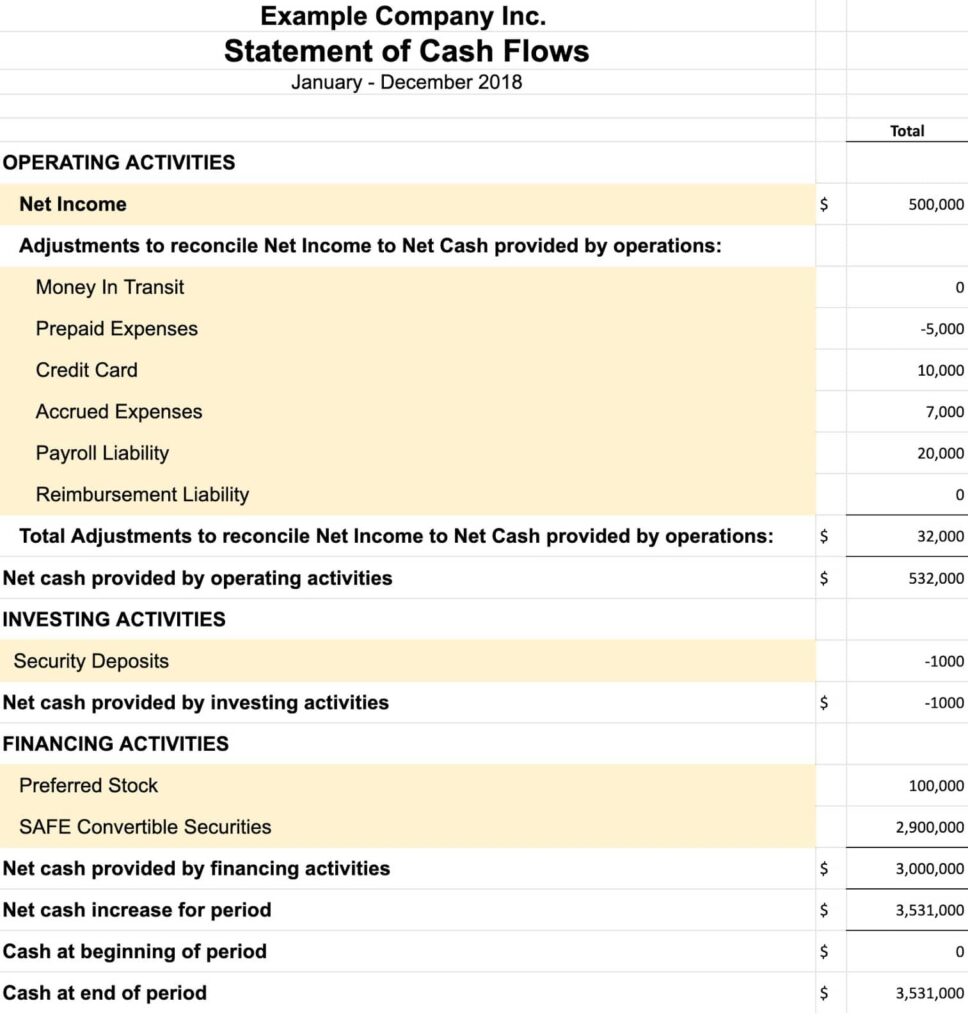
3. Cash flow report
The cash flow statement (CFS) provides an indication of how much cash the business has by examining how cash is moving in and out of the business. The three sections of the cash flow statement are cash from operating activities, cash from investing activities, and cash from financing activities. Altogether, the cash flow statement measures how well a company is generating cash to pay obligations and fund operations and investments.
A simple financial report template may look like something like this:
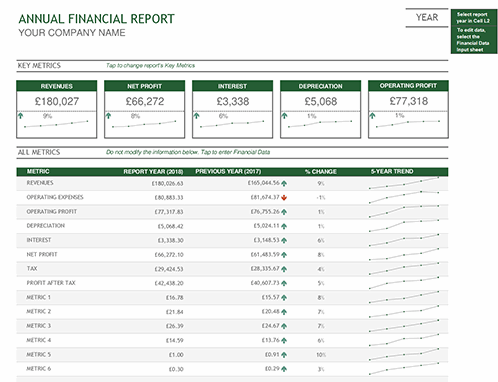
Why is financial reporting important?
Financial statements provide valuable information that helps investors and stakeholders alike evaluate how the company is doing. Beyond its informative nature, some of the key values of corporate financial reporting are:
Tax-related reasons
Financial reports are used to verify that an organization is paying the amount of taxes it should be paying.
Checking up on operations
Using reports such as the income statement, investors and stakeholders can determine an organization’s past income performance, as well as look into future expected behaviors.
Assisting with decision-making
When the c-suite needs to make a purchasing decision, they first start with assessing their current state. Decision-makers can look into assets and liabilities to determine whether a particular purchase is vital or possible.
How to create an optimal financial report
There are a few things to keep in mind when creating a financial report.
- Identify your purpose and audience
- Who are you reporting to? What are you trying to convey? Define your purpose and audience prior to putting together the report in order to optimize it. By taking your audience into account, you’ll be able to create reports that are tailored and suit their needs. Reporting internally or externally? To the CFO or general managers? These things matter and will influence how you formulate the information you need to present and how you choose to put together your report.
- Identify metrics
- Identify the KPIs that will best represent the financial stance of your company. You may choose to present the balance sheet, or alternatively the cash flow statement, depending on what point you’re trying to get across. You may also choose to present specific KPIs such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, or operating expense ratio.
- Visualize your data
- Average readers struggle to digest raw data. Make it easier to take in by representing it visually.
Financial reporting software can significantly assist organizations with their management reporting.
Financial reports often serve as the basis for more extensive reporting such as management reporting. Since this is the case, financial reports must be as accurate as possible – the future of the organization depends on it.
The production of management reports is a key responsibility of the FP&A function. Management reports are meant to keep decision makers up to speed on all the information they need to make better business decisions. Management reports draw on information from across the organization and tracks KPIs so that it is made very clear where things stand. One kind of management report that is delivered relatively consistently is the month-end report.
Today, top management expects the role of the finance function to evolve from providing pure financial information towards providing real insight based on an appropriate gathering and analysis of credible internal & external, finance & business information. Most companies also use ERP and CPM systems to benefit their companies’ IT Infrastructure.
Ad hoc reports are an important part of financial reporting.
FP&A is also responsible for the production of ad-hoc reports. When upper management has questions regarding a particular number or result, they may put in a request for a report that looks into it. This is where ad-hoc reports, or reports that are produced on a requested basis, come in.
Instead of relying on shaky foundations, organizations should do everything in their power to ensure that the foundations for decision making are solid. This is where financial automation comes in – financial reporting and analysis software that allows for the automatic creation of financial reports, such as Datarails, can help with ensuring that critical decisions are based on accurate and accessible numbers.
How can financial reporting teams leverage financial automation to improve processes?
FP&A teams typically spend a lot of time consolidating and formatting data instead of focusing on planning. This is where FP&A software can be of great help – by automating certain financial processes, FP&A professionals can focus their time on the part of their work with the greatest value-added- conducting analyses and investigations into the data.
Financial automation and financial analytics tools are a really great way to make the most of your finance function and the talent pool within it. Automated financial systems mean replacing manual processes with automated ones, which results in smoother processes. Instead of being slowed down by manual, error-prone processes, financial process automation accelerates procedures and saves you time.
Automating processes like consolidations and financial transformations can significantly boost the accuracy of your models and results. Data integrity is at much lesser a risk of being tainted as automation significantly reduces the risk of errors in calculations.
Present and report on results with financial dashboards
In order to gain a holistic view of the organization’s financial activities, working with a monthly, weekly, and daily financial report template can provide organizations with a well-rounded overview of every area of the business. Organizations need these reports in order to support financial objectives and provide meaningful information to all stakeholders including decision-makers, investors, etc.
One great way that FP&A teams can showcase their results is by using financial dashboards. Financial dashboards are a really great tool for visualizing your numbers, and they help you get a better sense of what the numbers are saying. Have sales increased significantly? Is one cost center vastly outperforming another? It’s one thing to take a look at the numbers, and it’s another thing to see the variances visually right in front of your eyes.
Financial reporting can be done better.
Datarails CPM solution allows you to create management reports and presentations that visualize your numbers without leaving the Excel platform you know and love. Directly feed data to Excel or Powerpoint, or vice-versa – Datarails’ unique Office-native integration pulls data from your unified database to Excel or Powerpoint. Watch as live embedded charts update figures on the spot, in real-time.
Filter through all your organizational data, whether it be from your GL, ERP, CRM, or Excel-based data, to generate reports that meet your specific needs. All your data is consolidated in one place, just select what you want to see.
Thanks to Datarails, watch your data transform into live charts with embedded, real-time visualizations. Compare any two or more metrics to better understand trends and cross-influence metrics. Then, create monthly managerial packages instantly that will be populated automatically for each month-end and send them to stakeholders.